Introduction
Polyethylene (PE) films are a cornerstone of modern packaging and manufacturing industries. With their diverse properties and wide-ranging applications, understanding the classification of PE films is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their operations.
This blog will explore the classification of PE films across four critical dimensions: density and molecular structure, processing techniques, functionality (including anti-static, easy tear, easy peel, protective, anti-fog, and composite features), and application range.
CloudFilm offers a complete PE film portfolio – including LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, CPE, MDO PE and BOPE films – to help converters, brand owners and trading companies match film structures to real packaging projects.
If you share your packed product, target markets and key film parameters (thickness, width, structure, barrier level), the CloudFilm team can quickly recommend suitable PE film types, arrange sample rolls and support your trials.

Density and Molecular Structure
The density and molecular structure of PE films significantly influence their physical properties and suitability for various applications. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers select the right type of film for their needs.
For a quick overview of CloudFilm’s PE portfolio by density, you can also visit the PE Film series, where LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, CPE, MDO PE and BOPE films are grouped for easier comparison.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Structure and Properties:
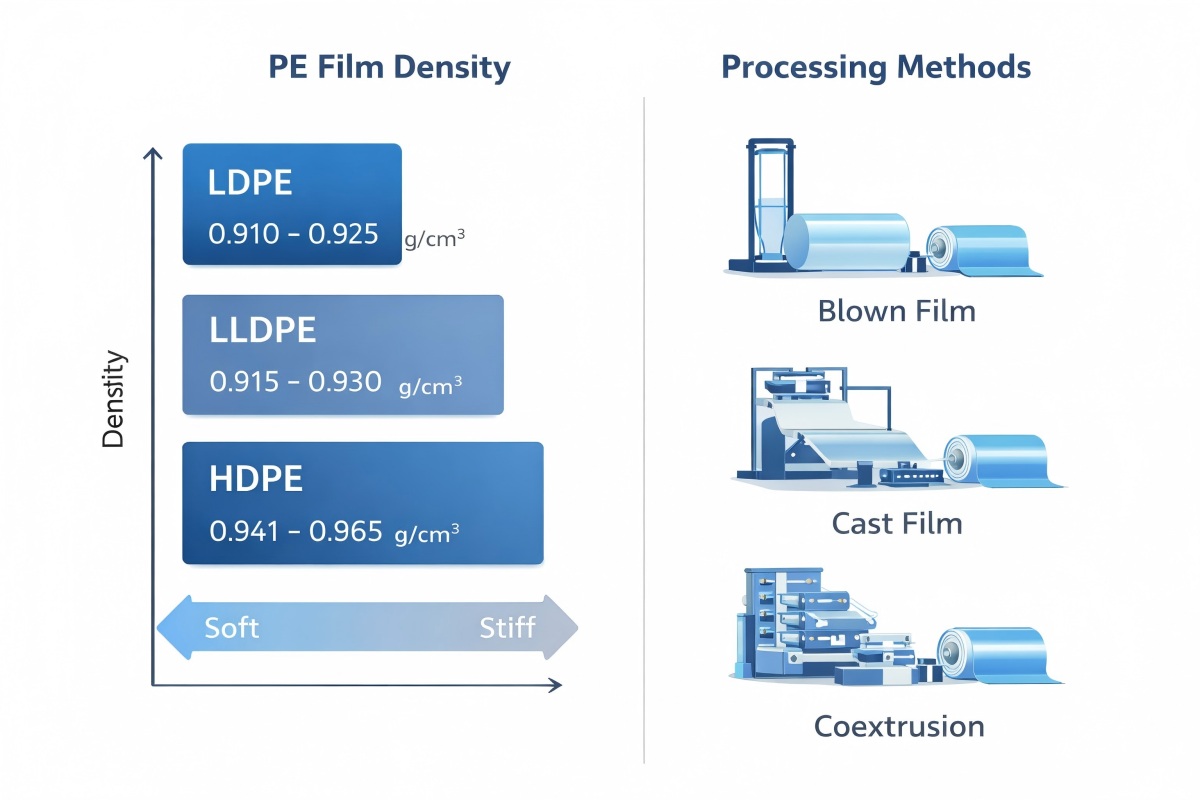
LDPE films are characterized by their highly branched molecular structure, which results in low density, high flexibility, and a soft feel. The density of LDPE typically ranges from 0.910 to 0.925 g/cm³. This structure contributes to its excellent elongation properties and resistance to impact, making it suitable for various packaging applications.
Common Applications:
LDPE films are widely used for grocery bags, food wraps, and other flexible packaging solutions. Their softness and transparency make them ideal for retail packaging, while their moisture resistance protects food products from spoilage.
Environmental Considerations:
While LDPE is recyclable, it poses challenges in recycling processes due to its low density. Efforts are ongoing to improve recycling methods and develop more sustainable LDPE products.
CloudFilm’s LDPE Film and Clear Poly Film can be customized in thickness, width and slip/anti-block levels, making them suitable as bags, liners or inner seal layers in PET/PE laminates.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
Structure and Properties:
LLDPE films are produced by copolymerizing ethylene with other alpha-olefins, resulting in a molecular structure that is more linear than LDPE. This structure enhances the film’s tensile strength, puncture resistance, and overall durability. LLDPE typically has a density ranging from 0.915 to 0.930 g/cm³.
Common Applications:
LLDPE films are primarily used in stretch films, agricultural films, and flexible packaging. Their enhanced strength makes them ideal for palletizing and securing goods during transportation.
Sustainability:
Similar to LDPE, LLDPE films can be recycled, and innovations in manufacturing are focused on reducing their environmental impact by incorporating post-consumer recycled content.
For stretch and agricultural applications, CloudFilm’s LLDPE Film and Silage Film offer good puncture resistance and optional UV-stabilized grades to withstand outdoor exposure.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Structure and Properties:
HDPE films feature a more linear structure with minimal branching, resulting in a higher density of 0.941 to 0.965 g/cm³. This structure gives HDPE films superior strength, rigidity, and resistance to impact and chemicals.
Common Applications:
HDPE films are used for heavy-duty applications such as industrial bags, containers, and packaging for hazardous materials. Their robustness makes them suitable for applications requiring a strong barrier against moisture and chemicals.
Recycling and Environmental Impact:
HDPE is widely recycled and can be repurposed into new products, contributing to a more sustainable lifecycle.
When you need stiffness, moisture barrier and chemical resistance, CloudFilm’s HDPE Film can be combined with PE Roll or high-barrier structures like PE PA PE Film for geomembranes, heavy-duty bags and construction covers.
Processing Techniques
The methods used to manufacture PE films significantly affect their properties, performance, and suitability for different applications. Here, we will explore the most common processing techniques.
Blown Film Extrusion
Overview:
Blown film extrusion is one of the most widely used methods for producing PE films. In this process, polyethylene is melted and inflated into a bubble, which is then cooled and flattened into a film.
Advantages:
- Barrier Properties: Blown films often exhibit excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, making them ideal for food packaging.
- Mechanical Strength: The orientation achieved during the blowing process enhances the tensile strength of the film, allowing for thinner gauges without sacrificing performance.
Applications:
Blown films are commonly used in food packaging, agricultural covers, and industrial applications due to their durability and barrier properties.
Cast Film Extrusion
Overview:
In cast film extrusion, molten polyethylene is extruded through a flat die and rapidly cooled on a chill roll to form a film. This technique produces smooth, clear films with excellent optical properties.
Advantages:
- Aesthetic Qualities: Cast films have superior clarity and gloss, making them suitable for applications where appearance is crucial.
- Thickness Control: This method allows for precise thickness control, resulting in consistent film quality.
Applications:
Cast films are often used for packaging, labels, and other applications where clarity and appearance are essential.
At CloudFilm, cast PE technology is widely used for CPE Film and laminating PE films that require high clarity, good flatness and stable thickness for printing and lamination.
Coextrusion
Overview:
Coextrusion combines multiple layers of different polymers during the manufacturing process, allowing for the creation of films with tailored properties.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Performance: By combining different materials, coextrusion can enhance barrier properties, sealability, and mechanical strength.
- Cost Efficiency: Coextruded films can offer performance characteristics of more expensive materials at a lower cost.
Applications:
Coextruded films are widely used in food packaging, medical applications, and industrial products, where specific properties are required.
CloudFilm can design coextruded structures such as BOPE/PE, MDO PE/PE or PA/PE to balance stiffness, seal strength and recyclability, depending on your project requirements.
Functionality
The functionality of PE films is crucial for meeting specific application needs. Here, we will examine various functional features, including anti-static, easy tear, easy peel, protective, anti-fog, and composite properties.
Anti-Static Films
Function and Importance:
Anti-static films are designed to reduce or eliminate static electricity buildup, which can damage sensitive electronic components. These films are treated with additives that dissipate static charges.
Applications:
- Powdered Food Packaging: These films are particularly useful in packaging powdered foods, preventing static that can cause clumping and ensuring product integrity.
- Electronics Packaging: Anti-static films are essential in the packaging of electronics, ensuring that products remain safe during handling and shipping.
- Medical Applications: These films are also used in medical device packaging to prevent electrostatic discharge that could damage sensitive equipment.
CloudFilm can incorporate anti-static additives into PE films or recommend specialty films such as CPP Anti Static Film when higher surface resistance control is required.
Easy Tear Films
Function and Importance:
Easy tear films are engineered to allow for convenient opening without the need for scissors or tools. They feature micro-perforations or specific film structures that enable quick tearing.
Applications:
- Food Packaging: Easy tear films are commonly used in snack packaging, allowing consumers to access products easily.
- Consumer Products: Many household items, such as cleaning supplies, also utilize easy tear technology for user convenience.
For more demanding easy-tear applications, CloudFilm also supplies Easy Tear Film that can be combined with PE sealant layers in laminates.
Easy Peel Films
Function and Importance:
Easy peel films are designed to separate easily from surfaces, providing a clean opening experience. These films are often treated with special coatings that facilitate peeling.
Applications:
- Ready-to-Eat Meals: Easy peel films are prevalent in food packaging, where convenience is a key factor for consumers.
- Labeling: These films are also used in labeling applications, ensuring that labels can be removed without leaving residue.
CloudFilm develops Easy Peel Film structures that can work with PP, PS or PET trays, offering controlled peel strength for dairy cups, ready-meal trays and snack packs.
PE Protective Films
Function and Importance:
PE protective films are designed to shield surfaces from scratches, dust, and other contaminants during manufacturing, transportation, and installation.
Applications:
- Electronics: Used to protect screens and surfaces of electronic devices.
- Industrial Equipment: Applied to machinery and components to prevent damage during handling and transit.
PE Anti-Fog Films
Function and Importance:
PE anti-fog films are engineered to prevent condensation and fogging, maintaining visibility in various applications. This is particularly important in food packaging and protective barriers.
Applications:
- Food Packaging: Used in packaging fresh produce and prepared foods to enhance visibility and presentation.
- Display Cases: Applied to display cases in retail environments to ensure clear visibility of products.
PE Lamination Films
Function and Importance:
PE composite films combine different materials to achieve enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved barrier properties or strength.
Applications:
- Multi-Layer Packaging: Used in food and medical packaging where multiple barriers are required.
- Specialty Applications: Employed in various industries where specific performance attributes are necessary.
Typical examples include CloudFilm’s PET/PE Film, PA/PE Film and PE PA PE Film, which combine PE seal layers with PET or PA for higher barrier and mechanical strength.
Application Range
The application of PE films spans various industries, each with specific requirements and challenges. Understanding these applications helps businesses select the most suitable film for their needs.

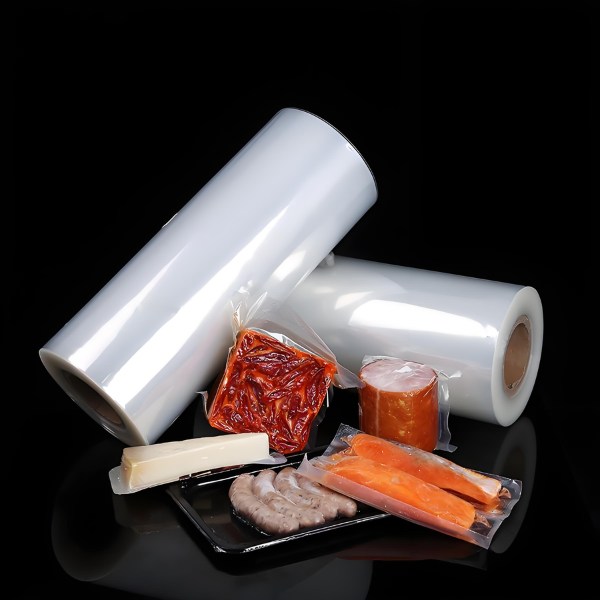
Food Packaging
Overview:
PE films are widely used in food packaging due to their ability to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. Their barrier properties protect against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants.
Types of Packaging:
- Flexible Packaging: Used for items such as snacks, frozen foods, and ready meals.
- Shrink Films: These films provide a snug fit around products, enhancing presentation and protection during transportation.
CloudFilm supplies food-contact PE films such as PE Shrink Film, PE Stretch Film and mono-PE solutions like BOPE Film for recyclable snack and frozen food packaging.
Agricultural Applications
Overview:
In agriculture, PE films play a vital role in improving crop yields and protecting plants from environmental factors.
Types of Applications:
- Greenhouse Films: These films control temperature and humidity, creating optimal growing conditions.
- Mulch Films: Used to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture, contributing to more efficient farming practices.
CloudFilm’s Silage Film and LLDPE-based agricultural films help farmers protect silage, control moisture and improve storage quality.
Industrial Applications
Overview:
PE films are employed in various industrial settings due to their strength and versatility.
Types of Applications:
- Protective Films: Used to protect surfaces during manufacturing processes.
- Insulation Films: Employed in the electronics and automotive industries for insulation purposes.
For industrial uses, CloudFilm offers PE Protective Film, Stretch Hood Film, VCI Film and PE Roll to secure pallets, protect surfaces and prevent corrosion.
How to Choose the Right PE Film with CloudFilm
Step 1 – Define your application and risk level (food, industry, agriculture, pharma)
Start by listing your packed product (e.g. snacks, frozen meat, detergents, construction materials), required shelf life, transport route and any special risks such as puncture, oil, chemicals or deep-freeze storage.
Step 2 – Choose base PE resin (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE) and structure type
For soft, clear packaging you may start with LDPE or LLDPE; for higher stiffness and moisture barrier you may consider HDPE or blends. Then decide whether you need a mono-PE structure (e.g. BOPE Film or MDO PE Film) or a laminate such as PET/PE Film or PA/PE Film.
Step 3 – Set key parameters: thickness, width, seal temperature, COF
Define your target thickness range, film width, seal temperature window, coefficient of friction and whether you need corona treatment for printing or lamination. These parameters ensure the film runs smoothly on your existing equipment.
Step 4 – Share your brief with CloudFilm for a quick proposal and samples
You can send a short project brief via the PE Film series or the “Get A Free Quote” form: product type, structure idea (e.g. mono-PE or PET/PE), thickness and width, annual volume and any special functions such as anti-fog, easy peel or anti-static. CloudFilm will respond with suggested structures and available sample rolls.

PE Film FAQs: CloudFilm Answers Common Questions
Q1. What is the main difference between LDPE, LLDPE and HDPE films?
LDPE is softer and more transparent, suitable for light-duty bags and inner seal layers. LLDPE offers higher strength and puncture resistance for stretch film, agricultural film and heavy bags. HDPE has the highest stiffness and moisture barrier, often used for heavy-duty liners, geomembranes and industrial packaging.
Q2. Which PE films does CloudFilm recommend for food packaging?
For pillow bags, pouches and lidding films, CloudFilm often combines PE with PET or PA using PET/PE Film
or PA/PE Film. For mono-PE and recyclable designs, BOPE Film and PE Shrink Film are popular choices.
Q3. Can CloudFilm develop custom PE structures such as PE/PA/PE or mono-material recyclable films?
Yes. CloudFilm regularly designs custom structures like PE PA PE Film, MDO PE Film and BOPE Film to support high-barrier, retort or recyclable packaging projects.
Q4. What information does CloudFilm need to quote a PE film project?
Please share your end use (food, industrial, agriculture, medical), planned structure (e.g. LDPE/LLDPE, PET/PE, PA/PE), target thickness and width, whether the film will be printed or laminated, required functions (anti-fog, easy peel, anti-static, VCI) and estimated order quantity. This allows CloudFilm to match a suitable grade and provide a clear quotation.
Q5. What are the typical MOQs and lead times for PE films from CloudFilm?
For most PE films, the typical minimum order quantity starts from around 1,000 kg per specification, and lead time depends on structure complexity, production load and printing requirements. The CloudFilm team will confirm exact MOQ and lead time after reviewing your specification.
Q6. Are CloudFilm PE films suitable for export markets in Europe, the Americas and other regions?
CloudFilm has long-term experience supplying flexible packaging films to customers in many countries. PE films can be produced according to the regulations and documentation requirements of different markets, and the team can provide technical data sheets and support for qualification.
Conclusion
Understanding the classification of PE films across density and molecular structure, processing techniques, functionality, and application range is essential for businesses in various industries. By selecting the appropriate film type, manufacturers can enhance product performance, meet consumer demands, and contribute to sustainable practices.
As innovations continue to shape the future of PE film technology, the potential for new applications and improved functionalities remains vast, making PE films an integral part of modern packaging and manufacturing solutions.
This comprehensive classification not only aids in informed decision-making but also emphasizes the importance of adaptability in an ever-evolving market landscape. As we look to the future, continued advancements in PE film technology promise to expand their utility, enhancing both performance and sustainability.