Introduction: Why Dry Food Packaging is Crucial?
Dry foods are a staple in our daily lives, ranging from breakfast cereals and snacks to pasta and pet food. Unlike fresh or frozen products, dry foods have unique preservation challenges that make packaging a critical factor in their success.
Proper dry food packaging not only protects the product from moisture, oxygen, light, and pests but also extends shelf life, maintains quality, and ensures food safety. In an increasingly competitive market, packaging also serves as a powerful marketing tool, communicating brand values and attracting consumers on crowded retail shelves.
Understanding Dry Food Packaging
1.1 The Unique Challenges of Dry Food Packaging 🛡️
Dry foods present specific packaging challenges that must be addressed:
- Moisture Protection: Even small amounts of moisture can lead to caking, mold growth, or texture changes.
- Oxygen Barrier: Oxidation can cause rancidity in nuts and seeds or loss of flavor in spices.
- Light Protection: UV light can degrade colors, flavors, and nutritional content.
- Pest Resistance: Packaging must prevent insect and rodent intrusion.
- Physical Protection: Preventing breakage, crushing, and abrasion during transportation and handling.
1.2 Main Types of Dry Food Packaging 📦
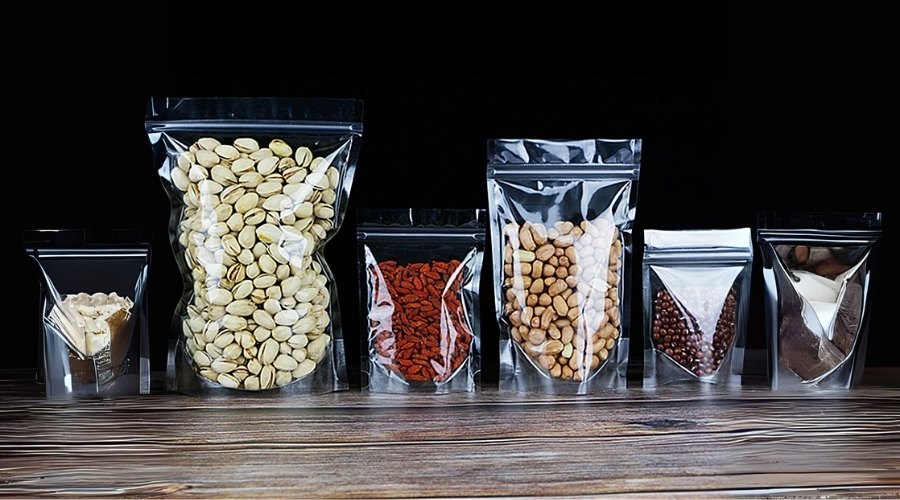
Flexible Packaging:
- Plastic bags (stand-up pouches, three-side seal bags, eight-side seal bags)
- Composite films (such as PET/PE, PET/AL/PE)
Semi-Rigid Packaging:
- Plastic trays + lidding films
- Plastic cans/boxes
Rigid Packaging:
- Metal cans (such as milk powder cans)
- Glass jars (such as some seasonings, dried goods)
- Paper boxes/cartons (often used as outer packaging or inner lining)
1.3 Regulatory Considerations ⚖️
Food packaging is subject to stringent regulations worldwide. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food contact materials, while the European Union has its own set of regulations under Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. These regulations ensure that packaging materials are safe for food contact and do not transfer harmful substances to the food.
Packaging Materials for Dry Foods
2.1 Plastics and Polymers 🔬
Plastics are the most commonly used materials for dry food packaging due to their versatility, barrier properties, and cost-effectiveness:
- Polyethylene (PE): Excellent moisture barrier, often used for inner layers.
- Polypropylene (PP): Good moisture barrier and high-temperature resistance.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Excellent gas barrier properties and clarity.
- Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol (EVOH): Superior oxygen barrier, often used in multi-layer structures.
- Polyamide (PA/Nylon): Good puncture resistance and oxygen barrier.
2.2 Aluminum and Metalized Films 🥫
Aluminum provides exceptional barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light:
- Aluminum Foil: Complete barrier to gases, moisture, and light, ideal for sensitive products.
- Metalized Films: Thin layer of aluminum deposited on plastic film, offering good barrier properties at lower cost and weight.
2.3 Paper and Paperboard 📄
Paper-based packaging is gaining popularity due to its sustainability credentials and aesthetic appeal:
- Kraft Paper: Offers a natural, eco-friendly appearance and is often used for bags and pouches.
- Paperboard: Provides rigidity and is commonly used for boxes, cartons, and composite cans.
- Barrier-coated Paper: Paper coated with plastic or other materials to improve barrier properties while maintaining recyclability.

2.2 Material Selection: Balancing Performance and Sustainability ⚖️
Choosing the right material is critical. Here’s a comparison of common options:
| Material | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic (PET, PP) | Lightweight, flexible, good barrier | Environmental concerns | Snacks, cereals |
| Aluminum Foil | Excellent barrier properties | Not recyclable in all areas | Coffee, powdered products |
| Paper-based | Eco-friendly, recyclable | Limited barrier properties | Dry fruits, nuts |
| Biodegradable Films | Sustainable, compostable | Higher cost, shorter shelf life | Organic products |
Packaging Formats and Technologies
3.1 Flexible Packaging Solutions 🧃
Flexible packaging has become increasingly popular for dry foods due to its lightweight nature, material efficiency, and consumer convenience:
- Stand-up Pouches: Provide excellent shelf presence and stability, with options for resealable zippers and spouts.
- Flat Pouches: Cost-effective solution for single-serve portions or samples.
- Quad Seal Bags: Offer excellent stability and high-quality appearance for premium products.
- Gusseted Bags: Expandable sides allow for larger volume capacity while maintaining a compact footprint.
3.2 Rigid and Semi-Rigid Options 🧴
Rigid and semi-rigid packaging provides enhanced protection and premium positioning:
- Plastic Tubs and Containers: Reusable and often resealable, ideal for products consumed over multiple servings.
- Composite Cans: Combination of paper body with metal ends, offering good barrier properties and premium feel.
- Jars and Bottles: Provide excellent barrier properties and are often perceived as premium packaging.
3.3 Advanced Packaging Technologies 🔮
Innovative technologies are enhancing the functionality and sustainability of dry food packaging:
- Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): Replaces air inside the package with a protective gas mixture to extend shelf life.
- Active Packaging: Incorporates substances that release or absorb compounds to maintain product quality.
- Intelligent Packaging: Includes indicators or sensors that monitor product quality or provide information to consumers.
- Nanotechnology: Enhances barrier properties through nano-scale materials and coatings.
Sustainability in Dry Food Packaging
4.1 Environmental Impact of Traditional Packaging 🌍
Traditional dry food packaging, particularly multi-layer flexible packaging, presents significant environmental challenges:
- Recyclability Issues: Multi-material structures are difficult to separate and recycle.
- Plastic Pollution: Single-use packaging contributes to plastic waste in landfills and oceans.
- Carbon Footprint: Production and transportation of packaging materials contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
4.2 Sustainable Packaging Alternatives 🌱
The industry is responding with innovative sustainable packaging solutions:
- Monomaterial Structures: Packaging made from a single type of plastic for easier recycling.
- Biodegradable and Compostable Materials: Plant-based materials that break down under appropriate conditions.
- Recycled Content: Incorporating post-consumer recycled (PCR) materials into new packaging.
- Lightweighting: Reducing material usage while maintaining performance.
4.3 Circular Economy Approaches ♻️
The packaging industry is shifting toward a circular economy model:
- Design for Recycling: Creating packaging that can be easily recycled at end-of-life.
- Refill Systems: Designing packaging for multiple uses through refill models.
- Packaging Recovery Programs: Implementing take-back and recycling initiatives.
Selecting the Right Packaging for Your Product
5.1 Product Characteristics Assessment 🧪
Selecting the right packaging begins with understanding your product’s specific needs:
- Moisture Sensitivity: Products like chips and crackers require high moisture barriers.
- Oxygen Sensitivity: Nuts and seeds need protection against oxidation to prevent rancidity.
- Fat Content: High-fat products may require additional barriers against flavor transfer.
- Aroma Retention: Products like coffee and spices need packaging that preserves volatile aromas.
- Particle Size and Shape: Fine powders versus whole pieces may require different packaging approaches.
5.2 Shelf Life Requirements ⏳
Determining your target shelf life will influence packaging material selection:
- Short Shelf Life (1-3 months): Basic barrier properties may suffice.
- Medium Shelf Life (3-12 months): Moderate barrier requirements with possible oxygen scavengers.
- Long Shelf Life (12+ months): High barrier materials with possible MAP technology.
5.3 Distribution and Retail Considerations 🚚
The journey from production to consumer impacts packaging requirements:
- Transportation Conditions: Distance, climate, and handling methods affect durability needs.
- Retail Environment: Shelf space constraints, display requirements, and competition.
- Consumer Usage: Portion control, resealability, and ease of use.
Future Trends in Dry Food Packaging
6.1 Smart and Interactive Packaging 📱
The future of dry food packaging includes intelligent features:
- QR Codes and NFC: Connect consumers to digital content, product information, and brand experiences.
- Time-Temperature Indicators: Visual indicators showing if products have been exposed to temperature abuse.
- Freshness Indicators: Sensors that change color to indicate product freshness or spoilage.
6.2 Personalization and Customization 🎨
Brands are leveraging packaging for personalized consumer experiences:
- Customized Printing: Digital printing enables cost-effective short runs and personalized designs.
- Shape and Format Innovation: Unique packaging structures that differentiate products on shelf.
- Targeted Functional Features: Packaging designed for specific consumer segments or usage occasions.
FAQs About Dry Food Packaging
Q1: What is the most sustainable packaging option for dry foods?
A1: The most sustainable option depends on your specific product requirements, but generally, monomaterial plastic packaging or paper-based options with appropriate barrier coatings offer good sustainability profiles. The key is to balance protection needs with end-of-life considerations.
Q2: How can I extend the shelf life of my dry food product?
A2: To extend shelf life, focus on three key areas: 1) Use high barrier materials appropriate for your product’s sensitivity, 2) Consider modified atmosphere packaging to replace oxygen with inert gases, and 3) Ensure proper sealing to prevent moisture and oxygen ingress throughout the product’s life.
Q3: What are the cost considerations when selecting dry food packaging?
A3: Packaging costs include material expenses, production efficiency, transportation costs, and marketing impact. While premium packaging may have higher upfront costs, it can reduce product waste, extend shelf life, and improve brand perception, potentially offering better overall value.
Q4: Can I make my dry food packaging resealable?
A5: Yes, many packaging formats can be made resealable. Options include zipper closures, adhesive tapes, peel-and-reseal labels, and snap-fit closures. The best choice depends on your product format, budget, and consumer usage patterns.
Conclusion: Finding Your Perfect Packaging Solution
Choosing the right dry food packaging involves balancing protection, sustainability, cost, and consumer appeal. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution—the best choice depends on your product, audience, and brand values.
At CloudFilm, we combine technical expertise with innovative solutions to help you find the perfect packaging. Whether you need sustainable materials, smart features, or custom designs, we’re here to help.
Ready to elevate your dry food packaging? Contact CloudFilm today for a consultation and samples!

















