Introduction: Meeting the Critical Need for Precision in Material Processing
In today’s advanced manufacturing landscape, the ability to precisely convert wide rolls of film material into narrower, usable widths is essential across countless industries. Film slitting – the industrial process of cutting large master rolls of film into multiple narrower rolls – serves as a fundamental operation in packaging, electronics, medical devices, and many other sectors. Film slitting refers specifically to the mechanical conversion of flexible materials through specialized cutting techniques.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about film slitting technology, from fundamental principles to advanced applications, helping you make informed decisions about your material processing needs.

Understanding Film Slitting: Core Concepts and Technical Parameters
What is Film Slitting?
Film slitting is a manufacturing process where wide rolls of film material are cut longitudinally to produce multiple narrower rolls with precise widths. This process is critical for converting large-scale production materials into formats suitable for downstream applications.
The precision of this operation directly impacts product quality, material utilization efficiency, and production economics.
Key technical parameters in film slitting include:
- Slitting accuracy: High-precision systems can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1mm
- Processing speed: Industrial slitters can operate at speeds exceeding 500 meters per minute
- Material compatibility: Effective for various films including plastic films(PET, PP, PE), metal foils, optical films, and laminated materials
- Tension control: Precise tension management prevents material deformation and ensures consistent winding
Three Primary Slitting Methods Compared
The choice of slitting method significantly impacts edge quality, production speed, and material waste. Below is a detailed comparison of the three most common slitting techniques:
| Slitting Method | Best Suited Materials | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Razor Slitting | Thin plastic films (<100μm) | Low cost, simple operation, high speed | Limited to thin materials, blade wear affects consistency |
| Shear Slitting | Medium to thick films, laminates | Clean edges, handles thicker materials, versatile | Higher initial cost, requires precise knife alignment |
| Score Slitting | Pressure-sensitive materials, adhesive films | No dust generation, suitable for sticky materials | Lower speed, may cause material deformation |
Table 1: Comparison of primary film slitting methods
Industrial Applications: Where Film Slitting Makes the Difference
Packaging Industry
The packaging sector represents the largest application area for film slitting services. Flexible packaging materials, including multi-layer laminates for food packaging, require precise slitting to ensure proper sealing performance and aesthetic appeal. Modern packaging films often incorporate barrier layers, printing, and special coatings that demand careful handling during the slitting process to maintain functionality.
Electronics and Optics
In electronics manufacturing, film slitting is critical for producing:
- Insulating films for capacitors and batteries
- Display components for smartphones and tablets
- Optical films for LCD panels and touchscreens
- Protective films for electronic components
These applications often require Class 1000 or better cleanroom environments to prevent contamination that could affect electronic performance.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Medical-grade films used in:
- Sterile packaging for medical devices
- Drug delivery systems
- Diagnostic components
- Wound care products
require stringent quality control and documentation throughout the slitting process to meet regulatory requirements.

Optimizing Your Film Slitting Process: Best Practices
Material Preparation and Handling
Proper material handling begins before the slitting process:
- Condition materials in the production environment for 24-48 hours to stabilize temperature and humidity
- Inspect master rolls for defects before processing
- Establish appropriate tension parameters based on material properties
Equipment Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance ensures consistent slitting quality:
- Daily: Clean cutting surfaces and remove debris
- Weekly: Check knife sharpness and alignment
- Monthly: Calibrate tension control systems and verify measurement accuracy
- Quarterly: Complete preventive maintenance on drives and bearings
Quality Control Measures
Implement these quality checks throughout the process:
- In-line width measurement using laser micrometers
- Edge quality inspection through vision systems
- Roll hardness testing to ensure uniform winding
- Tension verification to prevent telescoping or starring
Troubleshooting Common Film Slitting Challenges
Edge Quality Issues
Problem: Rough or jagged edges after slitting
Solutions:
- Verify knife sharpness and proper alignment
- Adjust cutting speed for material characteristics
- Consider alternative slitting methods for better edge quality
Material Wrinkling or Folding
Problem: Material folds during slitting or winding
Solutions:
- Optimize tension settings throughout the line
- Check roller alignment and parallelism
- Ensure proper unwind and rewind core positioning
Width Inconsistency
Problem: Variations in slit roll width
Solutions:
- Calibrate measurement systems regularly
- Verify knife positioning accuracy
- Check for material stretching or distortion during processing
Industry Trends and Future Developments
The film slitting industry continues to evolve with technological advancements:
Smart Manufacturing Integration
Modern slitting lines increasingly incorporate:
- IoT sensors for real-time process monitoring
- AI-powered vision systems for defect detection
- Predictive maintenance algorithms to minimize downtime
- Digital twin technology for process optimization
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental concerns drive innovation in:
- Energy-efficient slitting equipment designs
- Waste reduction through optimized cutting patterns
- Recycling programs for edge trim and unusable material
- Development of bio-based and recyclable films
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What factors determine the best slitting method for my material?
A1: Material thickness, composition, required edge quality, and production volume are key factors. Thin films generally work well with razor slitting, while thicker materials and laminates require shear slitting. Pressure-sensitive materials often benefit from score slitting.
Q2: How can I minimize material waste during slitting?
A2: Optimize cutting patterns, maintain sharp knives, implement proper tension control, and consider edge trim recycling programs. Advanced planning of roll layouts can significantly improve material utilization.
Q3: What tolerances can be achieved in precision film slitting?
A3: High-precision slitting systems can achieve tolerances of ±0.1mm for many materials. However, the achievable tolerance depends on material properties, thickness, and the specific slitting method used.
Q4: How often should slitting knives be replaced or sharpened?
A4: Knife maintenance frequency depends on material abrasiveness, production volume, and quality requirements. Generally, razor blades may need replacement daily to weekly, while shear knives can last several months with proper maintenance and regular sharpening.
Q5: Can film slitting be performed in a cleanroom environment?
A5: Yes, cleanroom film slitting is available for sensitive applications in electronics, medical devices, and optics. Cleanroom classifications from Class 100,000 to Class 1000 can be accommodated depending on product requirements.
Conclusion: Partnering for Precision in Film Slitting
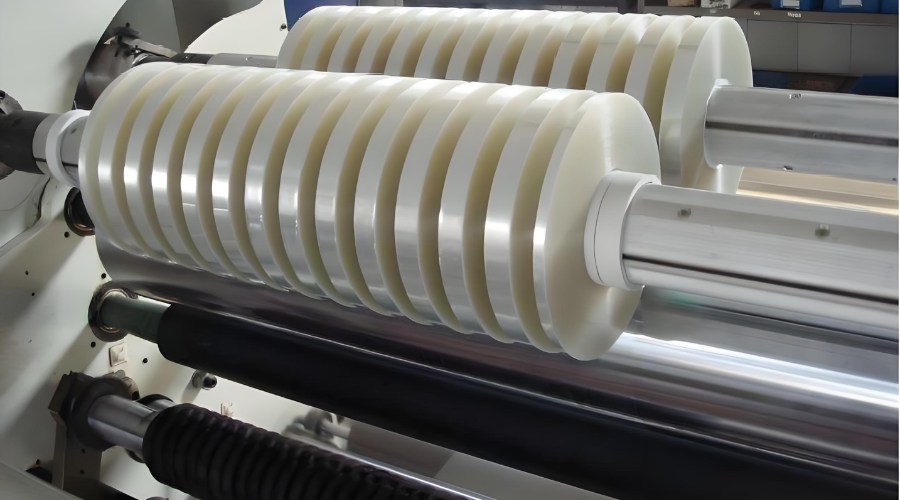
When your application demands precision film conversion, CloudFilm delivers specialized slitting services tailored to your exact specifications. Our advanced equipment and experienced team can handle materials down to 100mm widths with exceptional accuracy, ensuring your products meet the highest quality standards.
Contact us today to discuss your custom film slitting requirements.














