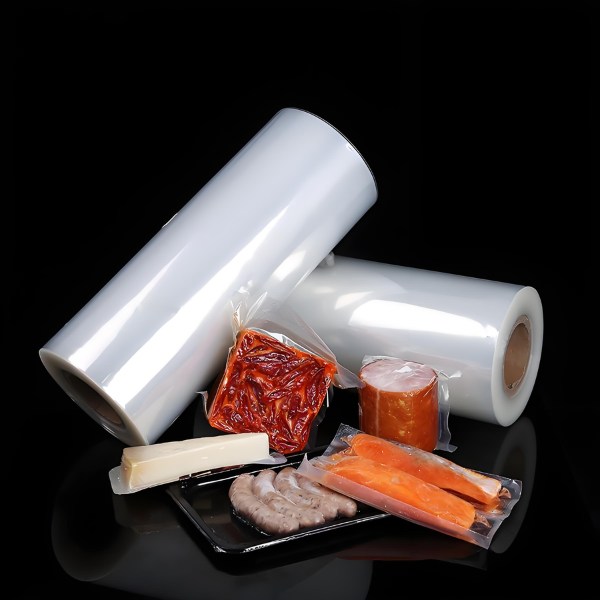
In the world of modern packaging, printing, and industrial applications, the term PE laminated is a cornerstone of material science. It refers to a multi-layered material where a layer of Polyethylene (PE) is bonded to another substrate, such as PET, aluminum foil, or paper.
This process isn’t just about sticking materials together; it’s about creating a new, high-performance material that combines the best properties of each layer.
At CloudFilm, we specialize in engineering these advanced PE laminated structures to solve complex challenges for businesses worldwide. 🚀
What is PE Laminated? The Core Concept Explained
At its simplest, “PE laminated” describes a composite material. Think of it like a high-tech sandwich. The “bread” could be a strong PET film, and the “filling” is a layer of PE. The PE layer is famous for its excellent heat-sealability, moisture barrier, and flexibility.
By laminating it to another material, we create a product that is not only strong and printable but also effectively protects its contents from moisture, oxygen, and contaminants.
For example, a common snack bag is often a PET/PE laminate. The outer PET layer provides strength, printability, and a glossy finish, while the inner PE layer allows the bag to be easily sealed shut, keeping the snacks fresh and crispy. Without the PE lamination, sealing the package would be much more difficult and less effective.
Why is PE the Go-To Choice for Lamination?
Polyethylene isn’t just a random plastic; it’s chosen for lamination for several critical reasons. Here’s a breakdown of its key advantages:
| Property | Benefit in Lamination | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent Heat Sealability | Creates a strong, airtight seal with heat and pressure, essential for packaging. |
Food pouches, medical device packaging. |
| Superior Moisture Barrier | Prevents water vapor from entering or exiting the package, protecting contents from humidity. |
Coffee, dried fruits, powders, electronics. |
| Flexibility & Durability | Adds a layer of toughness and puncture resistance without making the material rigid. |
Stand-up pouches, heavy-duty shipping sacks. |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists degradation from many oils, greases, and solvents. |
Industrial liners, chemical packaging. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | PE is a relatively low-cost resin, making the final composite material affordable. |
High-volume consumer goods packaging. |
Common Types of PE Laminated Structures
The magic of PE lamination lies in its versatility. By changing the layers we bond to PE, we can create materials with vastly different properties. Here are some of the most popular structures we produce at CloudFilm:
1. PET/PE Lamination
This is the workhorse of the flexible packaging industry.
- Structure: PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) + PE (Polyethylene)
- Key Features: High tensile strength, excellent printability on the PET side, and great heat-sealability on the PE side. Good barrier against gases and moisture.
- Typical Uses: Snack food bags, frozen food packaging, and lidding films. 🍟
2. Aluminum Foil/PE Lamination
When you need the ultimate barrier, this is the structure of choice.
- Structure: Aluminum Foil + PE (Polyethylene)
- Key Features: Provides a 100% barrier to light, oxygen, moisture, and gases. The PE layer allows for easy heat sealing.
- Typical Uses: Coffee packaging, pharmaceutical blister packs, and high-end cosmetic jars. ☕
3. Paper/PE Lamination
This structure combines the natural feel of paper with the functionality of plastic.
- Structure: Paper + PE (Polyethylene)
- Key Features: Offers a premium, eco-friendly aesthetic while providing moisture resistance and heat-sealability.
- Typical Uses: Paper cups for hot and cold beverages, food wrapping paper, and shopping bags. 📦
4. BOPP/PE Lamination
This is a cost-effective solution for high-clarity packaging.
- Structure: BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) + PE (Polyethylene)
- Key Features: Excellent clarity, high gloss, and good moisture barrier. Very economical.
- Typical Uses: Noodle packaging, bakery goods, and clear label films. 🍜
How is PE Laminated Material Made? A Simplified Process
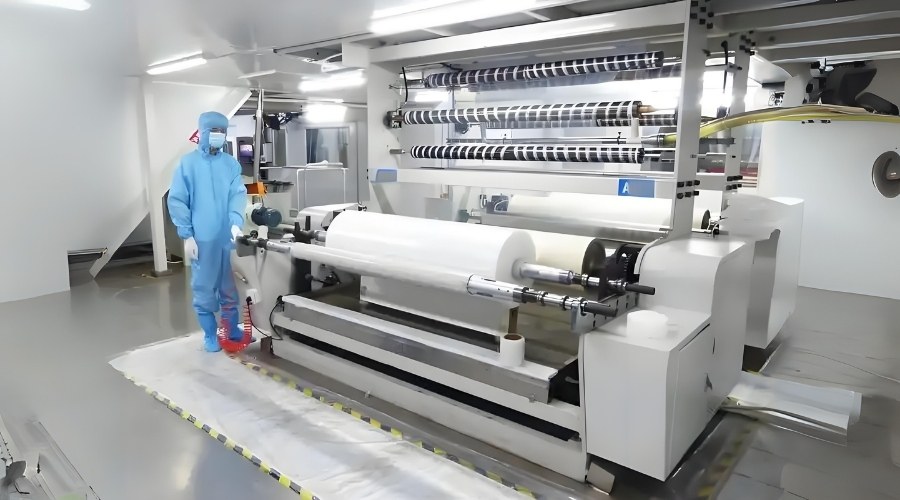

While the science is complex, the basic process can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Material Preparation: Rolls of the base material (e.g., PET, foil) and the PE film are loaded onto the lamination machine.
- Adhesive Application: A special adhesive is applied to one of the materials. This can be a solvent-based, solvent-free, or water-based adhesive, depending on the application and regulatory requirements.
- Bonding: The two materials are brought together under pressure, sandwiching the adhesive between them.
- Curing: The composite material passes through a drying oven (for solvent/water-based adhesives) or a curing chamber (for solvent-free adhesives). This step solidifies the bond, ensuring the layers are permanently fused.
- Winding & Slitting: The final, large roll of PE laminated material is wound up and then cut into smaller, more manageable rolls for the customer’s converting processes (like making bags or pouches).
The Future of PE Lamination: Innovation and Sustainability
The packaging industry is constantly evolving, and PE lamination is at the forefront of innovation, especially in sustainability. At CloudFilm, we are committed to leading this change. 🌱
- Recyclable PE Laminates: The biggest challenge has been recycling multi-material structures. New technologies are creating “mono-material” PE laminates where all layers are made of polyethylene variants, making the entire package fully recyclable in existing PE streams.
- Bio-Based and Compostable PE: We are exploring the use of PE derived from renewable resources (like sugarcane) and developing compostable laminates that break down under specific conditions.
- Downgauging: Through advanced engineering, we are creating thinner, lighter PE laminated films that use less plastic without sacrificing performance, reducing the environmental footprint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is PE laminated material recyclable?
A: Traditionally, multi-material laminates have been difficult to recycle. However, new all-PE structures are designed to be fully recyclable. It’s crucial to check with your supplier and local recycling facilities. At CloudFilm, we offer a range of recyclable PE laminate solutions.
Q2: What’s the difference between PE lamination and PP lamination?
A: The main difference lies in the properties of the sealant layer. PE offers superior heat-sealability at lower temperatures and a better moisture barrier. PP (Polypropylene) provides a higher temperature resistance and a stiffer feel. The choice depends on the product’s filling temperature and required barrier properties.
Q3: How do I choose the right PE laminated structure for my product?
A: The choice depends on several factors: your product’s sensitivity to oxygen/moisture, required shelf life, filling process (hot or cold), and desired aesthetics. The best approach is to consult with a material expert. Contact the CloudFilm team, and we’ll help you engineer the perfect solution for your needs. 📞